
Nmap is the most used tool for all types of hackers, especially the White Hat and System Administrators,
Nmap comes with many built-in scripts for various scans, that's why it became one of the popular hacking tools for hackers,
In this Nmap tutorial am going to tell you a short but effective tutorial on how to use Nmap and tell you the advanced Scanning Techniques that are not even told by many other Hackers.😇
Before we start you must have basic knowledge of IP/Networking and Nmap, if not then no need to worry I will try my best to explain more about Nmap Tool,
So in this post, I will be covering these
- Introduction To Nmap
- Nmap Basics
- Basic Target Scans
- Advanced Nmap Commands for Scanning
- Performance Optimization
- Nmap Script Engine
- Additional Resources
What is Nmap?
In simple words, Nmap is a Network Mapper, a free and open-source tool that comes with GUI and Command-line interface, and mostly used by IT Professionals to scan enterprise networks, so Nmap helps look for live hosts, specific services, or operating systems.How To Install Nmap
The Installation of Nmap is depended on your Operating System, in Linux it can be installed with a simple command,however we are skipping the installation guide as the installation process can be found on the official Nmap documentation,
the interesting thing is you can install Nmap on Android too, we have already published a tutorial on our blog, you can read it here,
Uses of Nmap
As I told you at the beginning of this tutorial, Nmap is a Network Mapper which helps us to scan a network/host and detect its open ports, closes ports, check a host is up or not and finally detecting the operating system the host is running and so on. this nmap tutorial will be little bit longer as we have tried to cover a lotBefore we start using Nmap, you must have basic knowledge of Networking,
Port Scanning: Before we do Port Scanning, you must be clear about what is a port,
a port is basically a way to connecting to a computer, there are over 65353 ports that can be open, closed and filtered
if a port is open that means the computer is listening for a connection.
if a port is close that means the computer is no longer looking for a connection in that port.
if the port is filtered then it is likely to be open or close and you should know that the system administrator hiding some sort of information.
Different Ports are used for different connections,
such as the common HTTP port is 8080, and
FTP port is 21 and so on, a port can be
easily identified as it comes after a colon eg:
127.0.0.1:8080, where 8080 is the port.
TCP and UDP protocols
these are the most commonly used protocols over a network. However these are used for listening for a connection, they play different roles
as
TCP Protocol
It is a Connection-oriented protocol, in simple words it is used for connections that need things to be ordered specifically, for example, loading a web page.
UDP Protocol
UDP Protocols are Connectionless protocol that doesn't assure the delivery of packets at the end, the most commonly used for Live Video Transforming.
Here is a quick overview of various types of Protocols
Various TCP/IP protocols
Application layer: FTP, HTTP, SNMP, BOOTP, DHCP
Transport layer: TCP, UDP, ICMP, IGMP
Network layer: ARP, IP, RARP
Datalink layer: SLIP, PPP
Now Let's use some Nmap commands for Port Scanning.
Before Performing Scanning through Nmap, you have to know the Different Scannings types.
you can get a list of commands with their uses by typing Nmap -h
It will print the help menu so that you can easily understand The Nmap Commands.
Now let's See How We can perform Different types of scanning Techniques using Nmap Commands,
Nmap host
eg:
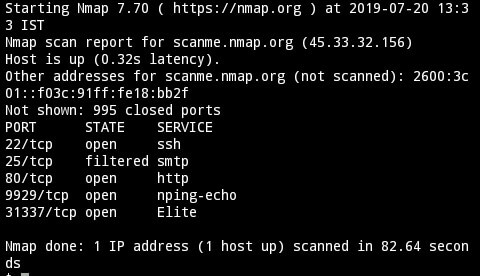
after executing the command you will see the results in real-time, it will show us the open ports, closed ports, filtered and even more.
To scan targets from a list the below command is used
Where targets.txt contains the targets
for that we have to do a service version scanning, it can be done very simply by adding a flag
it will output all the info regarding to the software versions along with ports,
Nmap usually supports three types of logging usually (.nmap, .gnmap, .xml)
The log files can be accessible in the command line also, just type ls and you will see the list of log files and
type cat logfilename.nmap to read it
Nmap command for logging scans
To Scan a Single port then it can be done by using the flag -p
Command: Nmap -p 21 scanme.nmap.org
It will scan only the FTP port and shows the port state.
For a Range of scan
Command:
Nmap -p 1-100 scanme.nmap.org
It will scan ports between the range 1-100
Scan The Common Ports Fast
Nmap -F scanme.nmap.org
It will scan for the most common ports fast.
Scan all 65535 Ports
While there might be several commands To Scan all the ports on the target below command is very easy to use
Nmap -p- scanme.nmap.org
To scan a subnet
Nmap scanme.nmap.org/24is used to scan the subnet
Ping Scan:
Nmap -sP scanme.nmap.org/24
we will discuss more in the advanced scanning section.
Now it's time to go with advanced scanning techniques, where you will find everything interesting.
TCP Connect: it works the same as SYN scan but it makes a full TCP connection, sometimes its results are more accurate than SYN scan.
Ping Sweep: This is a simple scan that Pings all the addresses to see which are responding to ICMP packets, however, this scan is not so accurate if the target machine is configured not to respond to a ping request.
UDP Scan: This scan is quite slow, and used to check whether any UPD ports are listening for a connection,
FIN Scan: It is just like an SYN scan but it sends a TCP FIN packet,
NULL Scan: This Scan Sets the TCP headers to null, this scan is helpful when the target is a non-Windows server and Protected by a firewall.
XMAS Scan: This Scan is Similar To Null Scan but it turns on the TCP Headers,
Bounce Scan: This scan is used on the FTP server to check if the target is Connected to LAN for breaching the FTP server and See the Connected Machines.
RPC Scan: This Scan Looks for machines that respond to Remote Commands,
Windows Scan: This type of scan is performed on Operating Systems if the ports supposed to be filtered.
Idle scan: This scan is performed if there the packets to the host is bounced off to an IP that you don't have control of it, this scan often used for malicious attacks,
Hope you guys gained some basic knowledge on How Nmap Scans works and the different types of Scans, Now let's see the Advanced Scanning Techniques
So let's see how to detect
Ping Sweep: Pinging is the most common method for detecting a host is up or not,
However, Nmap has a feature to do ping sweep against a host, the below command is used to perform ping sweep host detection.
Ping agnostic scan
When a system hides a host from ping sweep then a ping agnostic scan is used
Another thing is if you're scanning an SSL supported host then the flag -PS 443
is extremely useful for host detection.
As we told you earlier that UDP protocols are connectionless,
and it takes a little bit longer time to scan,
While scanning for UDP forts the flag -sU is used, moreover, it requires Root Privileges so sudo is a must
scans (-sT), the SYN stealth scan (-sS), FIN(-sF), Xmas Tree(-sX), and Null scan(-sN) Are extremely useful scanning techniques
The concept behind running these scans is that a closed port will attempt
to reset the connection by issuing an RST (reset) packet,
Note that FIN, Xmas,
and NULL scans are known to not work against Microsoft Windows hosts.
the flag -O is used to detect Target Os
By executing the command we will see the Operating System, MAC address(if we scan a LAN network), & OS CPE
-v Flag is Used For Verbose Scanning, and -vv Flag is the second level of verbose scanning and the final is -vvv Flag For High level verbose,
you can also use the --reduce-verbosity flag to reduce verbosity
This is also possible by using the flags traceroute and tcpdump but it is time-consuming.
so the flag --packet-trace is used for Packet Tracing
Timing Optimization is useful for quickly scanning a large network.
--min-hostgroup and --max-hostgroup flags are used for customizing host groups, note that it hosts group specification doesn't work at host discovery
The Flag --min-parallelism (use up to 10 or 1)2 makes Nmap scan even faster by reducing some of the risks,
similarly, the flag --max-parallelism (use as low as 1) makes Nmap scans slower.
to resolve that --host-timeout flag is used, 1 minute is enough but for a large enterprise 10 minute time out is better
Nmap scanme.nmap.org --host-timeout 1m
In This Section, let's see how we can use The Nmap Script Engine to conduct reconnaissance scans.
Before We Start Using Nmap Script Engine, Let me explain more about Nmap Script Engine,
Nmap Script Engine is Basically a Framework that runs in the programming language Lua, and on other hands Nmap script engine is a collection of scripts that are specifically coded for a purpose, to use the scripts we have to use the --scripts flag.
We strongly recommend you to read the Official NSE Doc By Nmap
The Nmap Scripts are basically categorised into the following
for that type this command
to use Nmap scripts --script script-name command is used,
Now its easier to run categorised Nmap scripts at once, below is a simple command for default scan with Nmap scripts
sudo nmap scanme.nmap.org --script defaut
If you want to scans by category or categories is too much, you can select scans by their specific name, or use wildcards. For example, if I wanted to scan a web server and load all the HTTP modules in the default scan repository, I would scan with the
--script "http-*" flag
eg:
😔 The Nmap Script Repository is quiet though, so it's better to do a little bit of practice, moreover, some security researchers develop their own scripts, keep updated with their scripts.
And therefore Nmap also can be integrated with Metasploit, Ncrack and many other Popular Framework,
➡ Nmap Cheat Sheet
➡ Nmap Mind Map
Thanks For Reading, Share this tutorial with your friends or forums and tell them that you learnt something better.
TCP and UDP protocols
these are the most commonly used protocols over a network. However these are used for listening for a connection, they play different roles
as
TCP Protocol
It is a Connection-oriented protocol, in simple words it is used for connections that need things to be ordered specifically, for example, loading a web page.
UDP Protocol
UDP Protocols are Connectionless protocol that doesn't assure the delivery of packets at the end, the most commonly used for Live Video Transforming.
Here is a quick overview of various types of Protocols
Various TCP/IP protocols
Application layer: FTP, HTTP, SNMP, BOOTP, DHCP
Transport layer: TCP, UDP, ICMP, IGMP
Network layer: ARP, IP, RARP
Datalink layer: SLIP, PPP
Now Let's use some Nmap commands for Port Scanning.
Before Performing Scanning through Nmap, you have to know the Different Scannings types.
Overview Of Nmap Commands
Since we are using Nmap In a Linux Command Line Interface, so we just have to know the Nmap Commands,you can get a list of commands with their uses by typing Nmap -h
It will print the help menu so that you can easily understand The Nmap Commands.
Now let's See How We can perform Different types of scanning Techniques using Nmap Commands,
Nmap Default Scan
For Running The Default scan the command is so easy thatNmap host
eg:
nmap scanme.nmap.org

after executing the command you will see the results in real-time, it will show us the open ports, closed ports, filtered and even more.
To scan targets from a list the below command is used
nmap -iL targets.txt
Where targets.txt contains the targets
Service Version Scanning
Sometimes we have to face a situation that we cannot determine which software is running on which version of the software.for that we have to do a service version scanning, it can be done very simply by adding a flag
nmap -sV scanme.nmap.org
it will output all the info regarding to the software versions along with ports,
Note:
However 65,535 ports can be open or closed but remember Nmap will scan only the top 1000 common ports only, for that, we will be covering some advanced scanning techniques, so keep reading.
However 65,535 ports can be open or closed but remember Nmap will scan only the top 1000 common ports only, for that, we will be covering some advanced scanning techniques, so keep reading.
Logging Scans
Sometimes Logging the Nmap scans is extremely useful when you're scanning a large network, it can be done by using the flag -oA logfile-nameNmap usually supports three types of logging usually (.nmap, .gnmap, .xml)
The log files can be accessible in the command line also, just type ls and you will see the list of log files and
type cat logfilename.nmap to read it
Nmap command for logging scans
nmap scanme.nmap.org -oA logfilename
Specific Scan Ranges
As we told you in the beginning that Nmap will scan only the top 1000 ports in a normal scan, we can set a range of scans or scan a specific port.To Scan a Single port then it can be done by using the flag -p
Command: Nmap -p 21 scanme.nmap.org
It will scan only the FTP port and shows the port state.
For a Range of scan
Command:
Nmap -p 1-100 scanme.nmap.org
It will scan ports between the range 1-100
Scan The Common Ports Fast
Nmap -F scanme.nmap.org
It will scan for the most common ports fast.
Scan all 65535 Ports
While there might be several commands To Scan all the ports on the target below command is very easy to use
Nmap -p- scanme.nmap.org
To scan a subnet
Nmap scanme.nmap.org/24is used to scan the subnet
Ping Scan:
Nmap -sP scanme.nmap.org/24
we will discuss more in the advanced scanning section.
Note:
However we did a small recap on Nmap but it takes time to be a master of Nmap,
If you still looking for Nmap commands then check out the Nmap manual by typing man Nmap on the command line or you can read it online here
However we did a small recap on Nmap but it takes time to be a master of Nmap,
If you still looking for Nmap commands then check out the Nmap manual by typing man Nmap on the command line or you can read it online here
Now it's time to go with advanced scanning techniques, where you will find everything interesting.
Nmap Advanced Scanning
Nmap Scan Types
SYN SCAN: This is the default scan by Nmap, in this type of scan Nmap Sends TCP SYN packets to each possible port. If it gets an SYN ACK packet back, then Nmap knows there is a service running there else it shows the port is closed.TCP Connect: it works the same as SYN scan but it makes a full TCP connection, sometimes its results are more accurate than SYN scan.
Ping Sweep: This is a simple scan that Pings all the addresses to see which are responding to ICMP packets, however, this scan is not so accurate if the target machine is configured not to respond to a ping request.
UDP Scan: This scan is quite slow, and used to check whether any UPD ports are listening for a connection,
FIN Scan: It is just like an SYN scan but it sends a TCP FIN packet,
NULL Scan: This Scan Sets the TCP headers to null, this scan is helpful when the target is a non-Windows server and Protected by a firewall.
XMAS Scan: This Scan is Similar To Null Scan but it turns on the TCP Headers,
Bounce Scan: This scan is used on the FTP server to check if the target is Connected to LAN for breaching the FTP server and See the Connected Machines.
RPC Scan: This Scan Looks for machines that respond to Remote Commands,
Windows Scan: This type of scan is performed on Operating Systems if the ports supposed to be filtered.
Idle scan: This scan is performed if there the packets to the host is bounced off to an IP that you don't have control of it, this scan often used for malicious attacks,
Hope you guys gained some basic knowledge on How Nmap Scans works and the different types of Scans, Now let's see the Advanced Scanning Techniques
Host detection methods
Before we start scanning the network we have to know whether the host is up or not. Nmap has several ways to detectSo let's see how to detect
Ping Sweep: Pinging is the most common method for detecting a host is up or not,
However, Nmap has a feature to do ping sweep against a host, the below command is used to perform ping sweep host detection.
nmap -sn scanme.nmap.orgThe flag -sn is used for ping sweep host detection.
Ping agnostic scan
When a system hides a host from ping sweep then a ping agnostic scan is used
nmap -Pn -n scanme.nmap.orgThe -Pn flag is used for a ping agnostic scan, sometimes the flag -sL list scan is extremely useful for DNS PTR record lookups
Another thing is if you're scanning an SSL supported host then the flag -PS 443
is extremely useful for host detection.
Scanning UDP services
While scanning for UDP forts the flag -sU is used, moreover, it requires Root Privileges so sudo is a must
sudo nmap -sU scanme.nmap.org
Special TCP Scans
As we have mentioned in different scan types the TCP connectscans (-sT), the SYN stealth scan (-sS), FIN(-sF), Xmas Tree(-sX), and Null scan(-sN) Are extremely useful scanning techniques
The concept behind running these scans is that a closed port will attempt
to reset the connection by issuing an RST (reset) packet,
Note that FIN, Xmas,
and NULL scans are known to not work against Microsoft Windows hosts.
Operating system detection
Sometimes we have to know which operating system the machine is running on, targets often run on multiple operating systems, however, Nmap can easily identify them.the flag -O is used to detect Target Os
sudo nmap -O scanme.nmap.org
By executing the command we will see the Operating System, MAC address(if we scan a LAN network), & OS CPE
Verbose Scanning
Verbose Scanning is used to retrieve information quickly while a scan is running, there are different levels of verbose scanning,-v Flag is Used For Verbose Scanning, and -vv Flag is the second level of verbose scanning and the final is -vvv Flag For High level verbose,
you can also use the --reduce-verbosity flag to reduce verbosity
Packet tracing
This Technique is used to understand the network hops that occur between hosts and to see the actual network traffic passing through.This is also possible by using the flags traceroute and tcpdump but it is time-consuming.
so the flag --packet-trace is used for Packet Tracing
sudo nmap scanme.nmap.org --packet-trace
Performance Optimization
We have already learnt how to scan using various techniques, but most of the time Nmap takes a longer time to scan, to reduce the scanning time let's learn how to use the advanced flags.Nmap timing optimization
To Make Scans Faster Nmap has some Flags -T1 to -T5, T1 is slower and T5 is higher, while the default is -T3Timing Optimization is useful for quickly scanning a large network.
nmap -T5 scanme.nmap.org
Customized host group sizes
Nmap uses a Group of hosts to scan the hosts efficiently,--min-hostgroup and --max-hostgroup flags are used for customizing host groups, note that it hosts group specification doesn't work at host discovery
Increasing and decreasing parallelism
You have to know how to customize host group size, however, there are flags used to increase or decrease parallelism in full scans, which helps Nmap to finish the scanning effectively.The Flag --min-parallelism (use up to 10 or 1)2 makes Nmap scan even faster by reducing some of the risks,
similarly, the flag --max-parallelism (use as low as 1) makes Nmap scans slower.
Dealing with stuck hosts
Commonly, sometimes hosts will be stuck while scanning a large enterprise, it happens if there was any security restrictions or something else that was stopping and slowing the scan.to resolve that --host-timeout flag is used, 1 minute is enough but for a large enterprise 10 minute time out is better
Nmap scanme.nmap.org --host-timeout 1m
Delaying and increasing probe rates
You can directly increase or decrease scan by using the flag --scan-delay it is a useful time-saving techniquenmap scanme.nmap.org --scan-delay 5s
Nmap Scripting Engine
So Far... We have Learnt How To Use Nmap for Port Scanning along With Advanced Nmap CommandsIn This Section, let's see how we can use The Nmap Script Engine to conduct reconnaissance scans.
Before We Start Using Nmap Script Engine, Let me explain more about Nmap Script Engine,
Nmap Script Engine is Basically a Framework that runs in the programming language Lua, and on other hands Nmap script engine is a collection of scripts that are specifically coded for a purpose, to use the scripts we have to use the --scripts flag.
Finding Nmap Scripts
Although The Scripts are Prepacked on your system the problem is you don't know which scripts to use,We strongly recommend you to read the Official NSE Doc By Nmap
The Nmap Scripts are basically categorised into the following
- Auth: These scripts attempt to authenticate to services, and can verify found credentials
- Broadcast: These scripts broadcast certain protocols to find out whether or not they are listening
- Brute: These scripts attempt brute force or dictionary-based attacks against network services
- Default: This is the default category of scripts that may run when a scan is initiated
- Discovery: These scripts attempt to enumerate sensitive information from hosts and network services
- Denial of Service (DoS): These scripts may cause disruption to the service that is being scanned
- Exploit: These scripts attempt to execute an exploit that exploits a given vulnerability
- External: These scripts query third-party databases, such as DNS blacklists, to gather additional information about targets
- Fuzzer: These scripts send random "garbage" information to services to attempt to find flaws in the software
- Intrusive: These scripts are an umbrella category for any script that may cause damage or be intrusive to the service itself
- Malware: These scripts attempt to find instances of the known malware.
- Safe: These scripts are verified to not cause harm to servers
- Version: These scripts attempt to identify specific versions as well as information disclosures from specific services in a more in-depth way than normal service version detection
- Vuln: These scripts identify the known vulnerabilities in services
Running Nmap Scripts
Running Nmap Scripts are very easy but before running them we have to check whether the Nmap script database is up to date or notfor that type this command
sudo nmap --script-update-dbonce the scripts database is updated then its time to use them
to use Nmap scripts --script script-name command is used,
Now its easier to run categorised Nmap scripts at once, below is a simple command for default scan with Nmap scripts
sudo nmap scanme.nmap.org --script defaut
If you want to scans by category or categories is too much, you can select scans by their specific name, or use wildcards. For example, if I wanted to scan a web server and load all the HTTP modules in the default scan repository, I would scan with the
--script "http-*" flag
eg:
sudo nmap scanme.nmap.org --script "http-*"
😔 The Nmap Script Repository is quiet though, so it's better to do a little bit of practice, moreover, some security researchers develop their own scripts, keep updated with their scripts.
And therefore Nmap also can be integrated with Metasploit, Ncrack and many other Popular Framework,
Additional Resources
➡ Nmap Cheat Sheet
➡ Nmap Mind Map
Conclusion
Although this is a Beginner Nmap Tutorial, we tried our best to explain still if you feel anything missed out then feel free to comment, so that in our next update we will include that,Thanks For Reading, Share this tutorial with your friends or forums and tell them that you learnt something better.